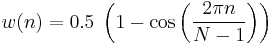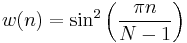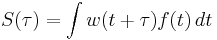Hann function
The Hann function, named after the Austrian meteorologist Julius von Hann, is a discrete probability mass function given by
or
Or, in terms of the haversine function, w(n) = haversin[2πn/(N-1)].
Contents |
Name
Hann function is the original name, in honour of von Hann; however, the erroneous 'Hanning' function is also heard of on occasion. The confusion arose from the similar Hamming function, named after Richard Hamming.
Use
The Hann function is typically used as a window function in digital signal processing to select a subset of a series of samples in order to perform a Fourier transform or other calculations.
i.e. (using continuous version to illustrate)
The advantage of the Hann window is very low aliasing, and the tradeoff is slightly decreased resolution (widening of the main lobe). If the Hann window is used to sample a signal in order to convert to frequency domain, it is complex to reconvert to the time domain without adding distortions.